The largest lake in the world is the Caspian Sea. Rivers flowing into the Caspian Sea: list, description, characteristics Where is the Caspian Sea located
The Caspian Sea is rightfully the most big lake on the entire planet and this sea-lake is located at the junction of two significant parts of the world: Asia and Europe.
There are still disagreements about the name of the Caspian Sea: is it a sea or a lake. And it is called the sea due to the large size of the reservoir.
Origin of the sea
The Caspian Sea is of oceanic origin. It was formed approximately 10 million years ago as a result of the division of the Sarmatian Sea.

According to one legend, the Caspian reservoir received its modern name in honor of the Caspian tribes living on the southwestern shores. Over all this time, the Caspian Sea has changed its name approximately 70 times.
Currents
The waters of the Caspian Sea can be divided into the following three parts:
- southern (39% of the area)
- medium (36% of total area)
- northern part (25% of the area).
The currents of a reservoir are formed as a result of the following influences: the general influence of the wind regime, differences in density in individual areas and the flow of inflowing rivers.

Along the western coast of the middle part of the Caspian Sea, southern and southeastern currents predominate. Depending on the direction of the winds, the middle and southern parts of the Caspian Sea are characterized by currents in the northern, northwestern, southern and southeastern directions. In the eastern part of the Caspian Sea, eastern currents predominate.
The following currents also play an important role in the circulation of Caspian waters:
- seiche;
- gradient;
- inertial.
What rivers flow into the Caspian Sea
The bulk of river waters enter the Caspian Sea through the Volga River. In addition to the Volga, the following rivers flow into this reservoir:
- Samur, flowing on the border of Azerbaijan and Russia;
- Astarachay, flowing on the border of Iran and Azerbaijan;
- Kura, located in Azerbaijan;
- Heraz, Sefudrud, Tejen, Polerud, Chalus, Babol and Gorgan flowing in Iran;
- Sulak, Kuma, located in the territory Russian Federation;
- Emba and Ural, flowing in Kazakhstan;
- Atrek, located in Turkmenistan.
 Sulak river photo
Sulak river photo
Where does the Caspian Sea flow into?
The Caspian reservoir has no connection with the ocean, since it is a closed reservoir. The Caspian Sea has dozens of bays. The largest of them can be distinguished: Komsomolets, Gyzlar, Kara-Bogaz-Gol, Mangyshlaksky, Kazakhsky, Krasnovodsky and others. Also in the waters of the Caspian Sea there are about 50 islands of different sizes, total area more than 350 km2. Some of the islands are united into archipelagos.
Relief
The following forms can be distinguished in the relief of the Caspian Sea bottom: in the south of the reservoir there are deep-sea depressions; a continental slope starting just below the shelf boundary and descending in the southern part of the Caspian to 750m, and in the middle part of the Caspian - up to 600m. shelf, the length of which from the depth to the coastline is 100 m and is covered with shell sands, and in deep water - with silty sediments.
 Derbent photo
Derbent photo
Coastline northern region The sea is low, quite indented, and flat in some areas. West Bank The reservoir is rugged, mountainous. In the east, the shores are distinguished by hills. South coastline mostly mountainous. The Caspian Sea is located in a zone of increased seismicity. Also, mud volcanoes often erupt here, most of which are located in the southern part of the reservoir.
Cities
The following states have access to the waters of the Caspian Sea:
- Russia. The largest city is Makhachkala, the capital of Dagestan. Also in Dagestan are the cities of Kaspiysk and Izberbash. In addition to the above cities in the Russian Federation on the Caspian Sea, it is necessary to note Derbent, the most southern city Russia located on west coast Caspian, Olya in Astrakhan region.
- Azerbaijan: The port city of Baku, the capital of Azerbaijan, is located in the southern part of the Absheron Peninsula. One more big city is Sugmait, located in the northern part of the peninsula. Also worth noting are the resorts of Nabran and Lankaran. The latter is located near the southern border of Azerbaijan.
- Turkmenistan with the port city of Turkmenbashi.
- Iran: Bandar-Torkemen, Anzali, Noushehr.
 Makhachkala photo
Makhachkala photo
Flora and fauna
All fauna The waters of the Caspian Sea can be divided conditionally into the following groups:
- The first group consists of descendants of ancient organisms: representatives of herrings (bellied, Volga, Kessler and Brazhnikovskaya herring); representatives of the Caspian gobies (golovach, puglovka, Berg, Baer, Knipovich and bubyr); sprat; a large number of crustaceans; some types of shellfish.
- The second group includes representatives of fauna that entered the sea from the north during the post-glacial era of desalination of the reservoir: seal; fish species: perch, carp, nelma, whitefish and brown trout; some representatives of crustaceans: sea cockroaches, mysid crustaceans and others.
- The third group includes species that entered the Caspian Sea from Mediterranean Sea: the following types of fish: singil, flounder and needle fish; representatives of mollusks; representatives of crustaceans: shrimps, amphipods, crabs.
- The fourth group includes representatives of freshwater fish that entered the Caspian Sea from fresh rivers: stellate sturgeon, beluga, sturgeon, Caspian fisherman, red-lipped asp, barbel, pike perch, catfish.
 sturgeon photo
sturgeon photo
The waters of the Caspian Sea are the main and main habitat for sturgeon representatives on the entire planet. Almost 80% of all sturgeon in the world live in the sea. Sharks and various predatory fish that pose any danger to humans do not live in this reservoir.
The flora of the Caspian Sea is represented by more than 700 species of lower plants (phytoplankton), as well as 5 species of higher ones (spiral and sea hornwort, comb pondweed, zoster, sea naiad). Here you can find various waterfowl. Some of them fly here for the winter from the north (waders, loons, gulls, geese, swans, ducks, geese), some fly from the south for nesting (eagles).

Characteristic
Let's get acquainted with the main characteristics of the Caspian Sea:
- The length from north to south was approximately 1200 km;
- The width of the basin from west to east is approximately 200-435 km;
- The total area of the Caspian Sea is approximately 390,000 km2;
- Volume sea waters- 78000 km3.
- The maximum sea depth is about 1025m.
- Water salinity averages up to 13.2%.
Sea level is located below the level of the World Ocean. The North of the Caspian Sea is characterized by a continental climate. The middle Caspian has a temperate climate. The southern part of the sea is characterized by a subtropical climate. in winter average temperature in the north it varies from 8 to 10 degrees below zero, and in the south from 8 to 10 degrees above zero. In summer, the average temperature in the north is 24-25 degrees above zero, and in the south 26-27 degrees Celsius.
 Caspian Sea. birds photo
Caspian Sea. birds photo
- To this day, scientists are debating: what status should the Caspian sea or lake be given? After all, this reservoir is closed and drainless. At the same time, this body of water prevails in size over some other seas.
- The bottom at the deepest point is separated from the water surface of the Caspian Sea by a distance more than a kilometer. The water level in the Caspian Sea is unstable and tends to decrease.
- This reservoir had approximately 70 names, which were given to it by different tribes and peoples living on its banks.
- There is a scientific theory that claims that the Caspian and Black Sea, were united into one sea in ancient times.
- The Volga River provides the Caspian Sea with most of the river water.
- Since the Caspian Sea is the main sturgeon habitat on the planet, most of the world's black caviar is produced here.
- The waters of the Caspian reservoir are constantly renewed every 250 years. The name of the reservoir, according to legend, comes from the name of the tribe that lived on its banks.
- The area of the Caspian Sea is larger than the area of Japan and slightly less than the area of Germany.
- If this body of water is considered a lake, it will take third place in depth in the world, after Baikal and Tanganyika. The Caspian is also the largest lake on the planet.
- The Caspian Sea is very rich in natural resources. Oil, gas, limestone, salts, clay, stones and sand are mined here.
- The Caspian Sea has recently faced the following environmental problems: Marine pollution. Oil is the main sea pollutant, suppressing the development of phytoplankton and phytobenthos. In addition to oil, phenols and heavy metals enter the Caspian Sea. All this leads to a decrease in oxygen production, resulting in death. large number fish and other organisms. Pollution also leads to illness of living organisms in the sea. Poaching is one of the main reasons for the sharp decline in sturgeon catches. Changes in natural biogeochemical cycles. Construction on the Volga deprives fish of natural habitats.
- The Caspian Sea is a very important object in the field of shipping and economics. This body of water is absolutely closed and isolated from the world ocean. This is the distinctive uniqueness of the Caspian Sea.
Caspian Sea- the most big lake on Earth, located at the junction of Europe and Asia, called the sea because of its size. Caspian Sea is a closed lake, and the water in it is salty, from 0.05% near the mouth of the Volga to 11-13% in the southeast.
The water level is subject to fluctuations, currently approximately 28 m below the level of the World Ocean.
Square Caspian Sea currently - approximately 371,000 km2, maximum depth - 1025 m.
Length of coastline Caspian Sea is estimated at approximately 6,500 - 6,700 kilometers, with islands - up to 7,000 kilometers. Shores Caspian Sea Most of its territory is low-lying and smooth. In the northern part, the coastline is indented by water channels and islands of the Volga and Ural deltas, the banks are low and swampy, and the water surface in many places is covered with thickets. On east coast Limestone coasts predominate, adjacent to semi-deserts and deserts. The most winding shores are on the western coast in the area of the Absheron Peninsula and on the eastern coast in the area of the Kazakh Gulf and Kara-Bogaz-Gol.
IN Caspian Sea 130 rivers flow in, of which 9 rivers have a delta-shaped mouth. Large rivers flowing into the Caspian Sea are the Volga, Terek (Russia), Ural, Emba (Kazakhstan), Kura (Azerbaijan), Samur (Russian border with Azerbaijan), Atrek (Turkmenistan) and others.
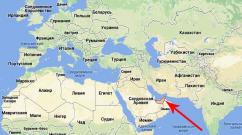
Map of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea washes the shores of five coastal states:
Russia (Dagestan, Kalmykia and Astrakhan region) - in the west and northwest, coastline length 695 kilometers
Kazakhstan - in the north, northeast and east, the length of the coastline is 2320 kilometers
Turkmenistan - in the southeast, the length of the coastline is 1200 kilometers
Iran - in the south, coastline length - 724 kilometers
Azerbaijan - in the southwest, the length of the coastline is 955 kilometers
Water temperature
is subject to significant latitudinal changes, most clearly expressed in winter, when the temperature varies from 0 - 0.5 °C at the ice edge in the north of the sea to 10 - 11 °C in the south, that is, the difference in water temperature is about 10 °C. For shallow water areas with depths less than 25 m, the annual amplitude can reach 25 - 26 °C. On average, the water temperature off the west coast is 1 - 2 °C higher than that on the east, and in the open sea the water temperature is 2 - 4 °C higher than off the coast.
Climate of the Caspian Sea- continental in the northern part, temperate in the middle part and subtropical in the southern part. In winter average monthly temperature The Caspian Sea varies from?8 ?10 in the northern part to +8 - +10 in the southern part, in summer period- from +24 - +25 in the northern part to +26 - +27 in the southern part. The maximum temperature recorded on the east coast was 44 degrees.
Animal world
The fauna of the Caspian Sea is represented by 1809 species, of which 415 are vertebrates. IN Caspian Sea 101 species of fish are registered, it also contains the majority of the world's sturgeon stocks, as well as such freshwater fish, like roach, carp, pike perch. Caspian Sea- habitat for fish such as carp, mullet, sprat, kutum, bream, salmon, perch, pike. IN Caspian Sea also inhabited by a marine mammal - the Caspian seal.
Flora
Flora Caspian Sea and its coastline is represented by 728 species. From plants to Caspian Sea The predominant algae are blue-green, diatoms, red, brown, characeae and others, and flowering algae include zoster and ruppia. By origin, the flora belongs mainly to the Neogene age, however, some plants were brought in Caspian Sea by a person knowingly or on the bottoms of ships.
Oil and gas production
IN Caspian Sea Many oil and gas fields are being developed. Proven oil resources in Caspian Sea are about 10 billion tons, the total resources of oil and gas condensate are estimated at 18 - 20 billion tons.
Oil production in Caspian Sea began in 1820, when the first oil well was drilled on the Absheron shelf. In the second half of the 19th century, oil production began on an industrial scale on the Absheron Peninsula, and then in other territories.
In addition to oil and gas production, on the coast Caspian Sea Salt, limestone, stone, sand, and clay are also mined on the Caspian shelf.
Environmental issues
Environmental issues Caspian Sea associated with water pollution as a result of oil production and transportation on the continental shelf, the flow of pollutants from the Volga and other rivers flowing into Caspian Sea, the life activity of coastal cities, as well as the flooding of individual objects due to rising levels Caspian Sea. Predatory production of sturgeon and their caviar, rampant poaching lead to a decrease in the number of sturgeon and to forced restrictions on their production and export.
The Caspian Sea is the largest lake on our planet, which is located in a depression of the earth’s surface (the so-called Aral-Caspian Lowland) on the territory of Russia, Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan and Iran. Although they consider it as a lake, because it is not connected with the World Ocean, but by the nature of the formation processes and history of origin, by its size, the Caspian Sea is a sea.
The area of the Caspian Sea is about 371 thousand km 2. The sea, stretching from north to south, has a length of about 1200 km and an average width of 320 km. The length of the coastline is about 7 thousand km. The Caspian Sea is located 28.5 m below the level of the World Ocean and its greatest depth is 1025 m. There are about 50 islands in the Caspian Sea, mostly small in area. The large islands include such islands as Tyuleniy, Kulaly, Zhiloy, Chechen, Artem, Ogurchinsky. There are also many bays in the sea, for example: Kizlyarsky, Komsomolets, Kazakhsky, Agrakhansky, etc.
The Caspian Sea is fed by more than 130 rivers. Largest quantity water (about 88% of the total flow) is brought by the rivers Ural, Volga, Terek, Emba, which flow into the northern part of the sea. About 7% of the flow comes from the large rivers Kura, Samur, Sulak and small ones that flow into the sea on the west coast. The rivers Heraz, Gorgan, and Sefidrud flow into the southern Iranian coast, bringing only 5% of the flow. Not a single river flows into the eastern part of the sea. The water in the Caspian Sea is salty, its salinity ranges from 0.3‰ to 13‰.
Shores of the Caspian Sea
The shores have different landscapes. The shores of the northern part of the sea are low and flat, surrounded by low-lying semi-desert and somewhat elevated desert. In the south, the shores are partly low-lying, they are bordered by a coastal lowland of a small area, behind which the Elburz ridge runs along the coast, which in some places comes close to the shore. In the west, the Greater Caucasus ranges approach the coast. In the east there is an abrasion coast, carved out of limestone, and semi-desert and desert plateaus approach it. The coastline changes greatly due to periodic fluctuations in water levels.
The climate of the Caspian Sea is different:
Continental in the north;
Moderate in the middle
Subtropical in the south.
At the same time, there are severe frosts and snowstorms on the northern shore, while fruit trees and magnolias bloom on the southern shore. In winter, strong storm winds rage at sea.
On the coast of the Caspian Sea there are large cities and ports: Baku, Lankaran, Turkmenbashi, Lagan, Makhachkala, Kaspiysk, Izberbash, Astrakhan, etc. 
The fauna of the Caspian Sea is represented by 1809 species of animals. More than 70 species of fish are found in the sea, including: herring, gobies, stellate sturgeon, sturgeon, beluga, white fish, sterlet, pike perch, carp, bream, roach, etc. Of the marine mammals, only the smallest in the world, the Caspian seal, is found in the lake. not found in other seas. The Caspian Sea lies on the main migratory route of birds between Asia, Europe and the Middle East. Every year, about 12 million birds fly over the Caspian Sea during migration, and another 5 million usually winter here.
Flora
The flora of the Caspian Sea and its coast includes 728 species. Basically, the sea is inhabited by algae: diatoms, blue-greens, red, characeae, brown and others, of the flowering ones - rupee and zoster.
The Caspian Sea is rich in reserves natural resources, many oil and gas fields are being developed in it, in addition, limestone, salt, sand, stone and clay are also mined here. The Caspian Sea is connected by the Volga-Don Canal with Sea of Azov, shipping is well developed. A lot of different fish are caught in the reservoir, including more than 90% of the world's sturgeon catch.
The Caspian Sea is also a recreation area; on its shores there are holiday homes, tourist centers and sanatoriums.
Related materials:
Caspian Sea is a unique ecological system. It is largest lake on planet Earth. Diverse biosphere, beautiful nature and wealth of natural resources make it attractive in all aspects.

Caspian Sea: description, photos and videos
Many people wonder what the area of the Caspian Sea is. This question is quite difficult to answer, since this parameter varies depending on seasonality. For example, when the water surface level is at 27 meters, the reservoir covers an area of 370 thousand square kilometers. This is almost 45 percent of the volume of freshwater lakes on Earth.
The Caspian Sea also has heterogeneous depth. In the north the maximum depth of the Caspian Sea only about 25 meters, and the average is within 4 meters. The southern region, on the contrary, is very deep - 1025 kilometers. This is the third highest figure in the world among lakes, after Tanganyika and. Scientists cannot yet name the exact reasons for such fluctuations in the Caspian Sea. Among the most likely versions is climate and crust change in the region.

Caspian Sea – Azerbaijan (Baku)
Since the lake is not only an industrial reservoir, but also a recreational one, the water temperature in the Caspian Sea is also of great interest. In winter, the lake experiences significant temperature changes. On the southern side it remains at 11 degrees, and on the northern side it can drop to 0.5 and below. Sometimes glaciation can be observed in this region.
During the summer period, which lasts here from early June to mid-September, the temperature is approximately the same throughout the entire reservoir. In the upper layers, the average values are kept within 26-27 degrees, and in shallow water the reservoir can heat up to 32. The water is slightly salted, but the saturation depends on the regional factor and may vary. The largest concentration is in the west and south, and in the northern part, thanks to freshwater rivers, it is the smallest. The local climate is also changeable.
The lake is located in three climatic zones at once:
- continental;
- moderate;
- subtropical.
Summers in the region are quite hot. The thermometer can reach up to 44 degrees Celsius. In winter in the south these indicators fluctuate up to +10, and in the north – up to -10. The Caspian Sea on the map has quite smooth shores, but in fact, its borders are very rugged with river mouths, peninsulas and straits. The length of the coast, including the islands, is 7 thousand kilometers. In the north, the coast is low and marshy areas caused by channels are common. In the east, limestones are common, flowing into semi-deserts.
There are approximately 50 islands on the lake. The largest of them:
- seal;
- Boyuk-Zira;
- Chechen;
- Ogurchinsky;
- Ashur-Ada.
Among the numerous bays one can note Kara-Bogaz-Gol. Until the end of the century before last, it was a kind of lagoon, but in 1980, construction of a dam began here, because of this, the amount of water entering the lake decreased. Today the strait has been restored.

What rivers flow into the Caspian Sea? The lake feeds a large number of rivers, the largest of which are:
- Volga;
- Sulak (Pro);
- Terek;
- Ural (Pro).
Every year they bring hundreds of cubic meters of fresh water into the lake.
The region has been actively developed for many centuries. Today on the Caspian Sea there are major ports connecting trade routes. Of the Russian ones, the most important are Astrakhan and Makhachkala. Oil production is also carried out in the Caspian Sea. According to experts, the region's oil resources amount to about 10 billion tons. There are also gas reserves here.
The Caspian Lake is an excellent place to relax. Local beaches amaze everyone who comes here. The quality of recreation on the Caspian Sea is in no way inferior. A pleasant climate, comfortable beaches and fresh air – the Caspian Sea is ready to give all this to tourists. Those who decide to visit the Caspian Sea can be pleasantly surprised by the prices for their holidays. You can get high-quality service for a low cost.
Popular cities include the following: resorts of the Caspian Sea:
- Makhachkala;
- Kaspiysk;
- Astrakhan;
- Lagan;
- Derbent;
- Dagestan lights.
Derbent is very attractive from a historical point of view. Astrakhan allows you to enjoy active recreation and fishing, and Makhachkala attracts with comfortable and equipped beaches. Holidays on the Caspian Sea in Russia allow you to restore your health and relax from the bustle of the city. Among foreign resorts the most popular are Baku (Azerbaijan), Avaza (Turkmenistan) and Aktau.
Caspian Sea on the map
Where is the Caspian Sea located? It is located on the continent of Eurasia. It is interesting that its eastern coast is located in Asia, and its western coast is in Europe. Conventionally, the sea is divided into several parts:
- Northern Caspian;
- South Caspian;
- Middle Caspian.
Of these, only the Northern Caspian is a sea shelf. It contains only 1 percent of the total volume of water and ends at Chechen Island, located near the Kizlyar Bay.
Which countries is washed by the Caspian Sea? There are 5 states on the shore of the lake:
- Azerbaijan;
- Iran;
- Turkmenistan;
- Kazakhstan;
- Russia.
The largest coastline runs through the territory of Kazakhstan; in second place, according to this indicator, is Russia. The coast of Azerbaijan has the shortest length, but it owns the largest port - Baku.
There are also other large settlements on the coast of the salt reservoir:
- Anzeli (Iran) – 111 thousand people;
- Aktau (Kazakhstan) – 178 thousand people;
- Atyrau (Russia) – 183 thousand people
Astrakhan also belongs to the coastal cities of the Caspian Sea, although the city is located 69 kilometers from the coast. Other Russian cities on the seashore include Makhachkala, Derbent and Kaspiysk.
Caspian Sea or lake?
The Caspian Sea is geographical feature, the essence of which does not quite correlate with its name.
Why is the Caspian Sea considered a lake? Caspian Sea is a closed and closed reservoir. It receives water from rivers and has no connection with the oceans or other seas. Although the water here is salty, this indicator is significantly lower than that of other seas. The Caspian Sea is not subject to international maritime laws.
On the other hand, the Caspian Sea is quite large in size, differing from traditional ideas about lakes. Even Baikal, and even more so, is inferior to it in area. There are no other lakes in the world whose coast simultaneously belongs to five states. The structure of the bottom is also very similar to the oceanic type. With a high degree of probability, the waters of the Caspian Sea flowed into the Mediterranean Sea many centuries ago, but due to drying out and tectonic processes, they were separated.
The Caspian Sea is rich in islands, the size of which, even by international standards, is quite large.
Nature of the Caspian Sea
One of the most interesting riddles Caspian Sea - living on the territory of the lake is a population of seals, which are a small variety of those that live in the cold northern waters. However, their appearance on the coast at least indicates that these places are beginning to recover ecologically after the negative consequences of oil production.
The flora and fauna of the Caspian Sea are very diverse. The underwater ecosystem boasts a large number of crustaceans, mollusks, gobies, herring and sprat. Many species are endemic, meaning they live only in this region and nowhere else.
Freshwater species also live in the waters of the lake. They were able to adapt to salt water. These are primarily carp and perch fish. At the end of the Ice Age, Arctic fish and invertebrates entered here. In the 40s of the last century, the waters of the Caspian Sea were deliberately populated with mullet, nereis and abra, which are the food source for sturgeon.




In the vicinity of the Caspian Sea, there are fish processing plants, as well as treatment stations designed to ensure water circulation cycles. Systematic work is also underway to breed many varieties of underwater abodes that have industrial value. The region is of great interest for fishing tourism. This holiday is especially popular in the Astrakhan region on the Caspian Sea.
The flora of the lake is represented by more than 700 plant species. Some of them grow on land, others in water. The phytoplankton of the Caspian Sea consists of both marine and freshwater algae. According to rough estimates, about 440 species of algae live in the reservoir.
Historical facts
The Caspian coast was once home to ancient civilization, which subsequently disappeared. There is an opinion that in the vicinity of Dagestan, the waters hide from human eyes Itil, the capital city of the Khazar Khaganate, which completely disappeared in the 12th century. In Derbent there is still a wall from ancient settlement, going to a depth of 300 meters. For what purpose it was built and who built it is a mystery.
One more interesting feature Caspian Sea – Sabail citadel, located underwater in Baku Bay. The structure was flooded during an earthquake that occurred in 1306. In 1723 the upper part of the high tower became visible above the water surface - this was a consequence of the decrease in water level. Today, the fortress is again hidden in the depths of the Caspian Sea, although in sunny weather it can be seen in the water column.
The territory of the Caspian Sea was a “bone of discord” between adjacent countries. Disputes over the distribution of ownership and resources of the lake continued for 22 years. In 2018, the countries finally came to a common denominator. On August 12, the Convention on the Legal Status of the Caspian Sea was signed. Before this, in the legal field, regulation was carried out on the basis of Soviet-Iranian agreements defining the Caspian Sea as a closed body of water, and each border state had an independent right to a 10-mile zone. The rest of the lake was divided equally.
How the Caspian Sea was divided? The new agreement assigns 15 miles of territorial waters to each state. Also, the bottom of the Caspian Sea is divided into sectors, as happens with the seas, and the sovereignty of the water column is established according to the lake principle.
For the current day Caspian Sea is an economically important region. It is impossible to imagine Eurasia, including Russia, without it. Everyone should visit the Caspian Sea, and the protection of the reservoir should be carried out at the state level. Only through joint efforts can we preserve this natural pearl.
The Caspian Sea is located on the continent of Eurasia. The surprising thing is that the Caspian Sea, with an area of 370 thousand square kilometers, is actually the largest lake, since it has no connection with the ocean. Although it is difficult to call it a lake, because the composition of the water, flora and fauna are similar to those of the sea. The salinity of the water is close to oceanic (from 0.05% to 13%).
Photo: Seagulls on the shores of the Caspian Sea.
 About 50 million years ago, the Tethys Sea was located on the territory of Eastern Europe, which, when drying up, was divided into several large bodies of water - the Caspian, Black and Mediterranean seas.
About 50 million years ago, the Tethys Sea was located on the territory of Eastern Europe, which, when drying up, was divided into several large bodies of water - the Caspian, Black and Mediterranean seas.
Thanks to mineral waters And therapeutic mud The Caspian Sea has great recreational and health potential. Therefore, there is an increase in the popularity of the coasts of Turkmenistan, Iran, Azerbaijan and Russian Dagestan among tourists.

Particularly popular is the resort area in the Baku region, where the popular resort in Amburan, as well as the area of the village of Nardaran, sanatoriums in the villages of Zagulba and Bilgah. In the north of Azerbaijan, the resort in Nabran is gaining popularity.

Unfortunately, tourism in Turkmenistan is poorly developed, which is due to the policy of isolation. And in Iran, Sharia law prohibits foreign tourists from vacationing on the coast.

But if you decide to relax on the Caspian Lake, then you will enjoy walking through protected areas; you will see extraordinary floating islands, various plants and animals that live in fresh and salt waters.

There is a greater variety of ways to have a good time throughout the year. For example, you can go on boat cruises, go fishing or waterfowl hunting, or you can simply enjoy the healing waters, looking at seals and a variety of birds. The protected areas of the sea coast are very beautiful, for example the Astrakhan International Biosphere Reserve and the Volga delta with lotus fields.

A special feature of the Caspian zone is oriental flavor with hookah and mesmerizing dancing. Traditional music will delight your ears, and East Asian cuisine will satisfy your hunger.

See where the Caspian Sea is located on the world map.
Sorry, the card is temporarily unavailable Sorry, the card is temporarily unavailable
Video: Caspian Sea. Storm. 07/08/2012.