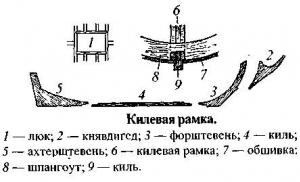
Technical characteristics of the boat micron drawing of transom reinforcement. Motorboat "MKM"
| Basic data of the MKM motorboat | |
|---|---|
| Maximum length, m | 4,10 |
| Maximum width, m | 1,52 |
| Side height at midship, m | 0,57 |
| Bottom deadrise angle at transom | 2° |
| Weight with equipment and supplies, kg | 150 |
| Load capacity, kg | 400 |
| Passenger capacity, persons | 4 |
| Permissible PM power, l. With. | 25 |
| Speed under the engine is 25 HP. With. with full load, km/h | 32 |
Duralumin release motorboats "MKM", designed by the Yaroslavl Shipyard, was started in 1968 at several shipyards. Due to its higher stability, hull strength and freeboard height, this boat was supposed to replace the Kazanka-type motorboat, which turned out to be insufficiently safe when installing outboard motors with a power of over 12 hp. With. At the same time, the hull design and equipment of the boat were made similar to the Kazanka, the only standard industrial motorboat made of light alloys produced in the USSR at that time. The prototype for the theoretical drawing was the MK-29 motorboat, which has flat-keeled bottom contours with a low deadrise and a slight slope of the sides inward at the transom.
General location of the MKM motorboat
The body is of riveted construction made of D16AT duralumin, the set parts are stamped from AMg5M aluminum-magnesium alloy and duralumin profiles. The thickness of the bottom and deck plating is 1 mm. The framing system is mixed with six frames and longitudinal stringers along the bottom. The forepeak and engine compartment are separated from the cockpit by watertight bulkheads. When parked, an outboard motor can be placed in the engine compartment and the compartment is closed on top with metal covers. The forepeak with a volume of 168 liters together with a 90 liter sealed box under the stern can provides.

The boat is equipped with three transverse banks, a windshield, and wooden slatted slats. The two bow seats are equipped with reclining backrests. Below the deck in the bow there is a small trunk with a lockable lid in the bulkhead. Operation of the boat is allowed at a wave height of up to 0.25 m and a distance from the shore of up to 1000 m. When sailing in rough seas, the boat gets heavily splashed due to the low deadrise of the bottom, the low location of the chine in the bow and the absence of bilge splash guards. Due to the existing downward bend of the bottom at the transom, the MKM buries itself in the wave and tends to tip over the chine. To eliminate these shortcomings, the consultants of the Boats and Yachts magazine recommended the installation of bilge splash guards and a transverse step. The plant made attempts to organize the production of deckhouses for the MKM motorboat, but things did not go further than prototypes. The MKM boat can be recommended for fishing with motors of the Moskva and Veterok types and for walks with more powerful motors.
In general, the MKM boat turned out to be unsuccessful. Its seaworthiness and operational safety are no better than those of the Kazanka. In addition, the MKM does not have any “zest”, that is, any positive qualities that would allow, under certain operating conditions, to give preference to the MKM over other boats.
With the advent of 20-horsepower outboard motors, the question arose about the need to replace practically the only motor boat at that time, “Kazanka”: it was still produced in large series, but was no longer suitable for operation with such motors. As a replacement, the shipbuilders proposed a metal version of the previously popular plywood motorboat “MK-29” designed by E. E. Kloss. The theoretical drawing was completely borrowed from this project, the hull design was copied from the Kazanka - this is how the wider and higher-sided (seemingly more seaworthy!) MKM appeared, for the construction of which in 1967-1969. seven factories took over at once!
Soon, after modernization and a corresponding increase in the price of the “Kazanka” with boules - the “MD” model was already sold at a price of 400 rubles, the “MKM” became the cheapest “motorboat”: the retail price of most boats was 370 rubles. (Note that some building factories, not adapted to large-scale production of boats, were forced to sell MKM at more high price- up to 450 rub.; while the expensive boat was no more different high quality manufacturing, nor any additions to the equipment.)
What can you say about the MKM contours? Its theoretical drawing () was developed almost 20 years ago with the expectation of operation mainly with the 10-horsepower Moskva, under which the MK-29, which had a light, 70-kilogram body, reached a maximum speed of 30 km/h. With a load of 3-4 people, the boat was moving in a transitional mode to planing, therefore, in order to increase its hydrodynamic qualities, it was necessary to increase the width of the bottom and limit the deadrise angle to a minimum value (at the transom - 4°). The bending of the bottom down at the transom also contributed to the planing and reduction of the running trim. Thanks to this bend, the size of which is the same on the MK-29 and MKM and is 8 mm, the aft section of the bottom turns out to be located at a greater angle of attack to the oncoming water flow than the middle of the hull; here a significant lifting force is created, which lifts the stern and “puts” the bow of the boat on the water.
But what was good for the 10-horsepower Moskva turned out to be significant disadvantages when installing the twice as powerful Whirlwind and Msskva-25 on the same boat. It is well known that a boat with a wide and flat bottom planes at a minimum angle of attack, and the MKM also has the effect of bending the bottom. Therefore, when meeting even a small wave, clouds of spray burst out from under the low-slung chine of this boat and fall on the heads of the passengers and the driver of the boat. Attempts to raise the bow - to increase the running trim aft, giving the boat a stern load - have no effect. You can often see how the MKM is controlled while sitting on the transom itself and lowering its feet into the engine compartment. And the reader of the collection, Petrushko from Novochebok-sarsk, tried to improve the seaworthiness of the boat by loading the engine compartment to the top with raw sand; against the wave, the boat actually went better, but its speed dropped by almost half.
V.V. Borodenko from Saratov made an external bracket behind the transom of his MKM, on which he hung two Neptunes, installed longitudinal steps and zygomatic splash guards, moved the boat control station to the stern and placed 4 cans of fuel here. And all this taken together could not “tear off” the bow end of the boat from the water or significantly improve its performance on the wave.
It goes without saying that attempts to equip the MKM with a remote control with a steering wheel in the forward part of the cockpit - near the windshield - further aggravated the existing disadvantage. The boat not only did not float to the oncoming wave, but crashed into it, losing speed. It is not surprising that, despite the large width and significant stability of the MKM, from time to time there are cases of boats of this type capsizing: after all, to do this, it is enough to make a sharp movement with the tiller on a passing or side wave...
Needless to say about the strong blows that a flat-bottomed boat receives when sailing against a wave, the uncomfortable engine compartment, the lack of an awning and a fragile windshield, and the hopelessly outdated design. It is very good that to date the production of “MKM” has been discontinued at five factories, but two enterprises continue to produce this far from perfect model this year.
Well, what to do with tens of thousands of MKMs already in personal use?
If we leave aside the incorrigible shortcomings inherent in the MKM, as in any boat with a flat bottom of low deadrise, then we can say that the “root of evil” is the bend of the bottom at the transom. Therefore, first of all it is necessary to either get rid of this limb or neutralize its effect.
To eliminate the bend of the bottom, it is necessary to unstitch the rivet seams securing the bottom and side skin along the cheekbone, as well as to the bottom stringers and keel, starting from the transom to the second frame from the stern. The lower edge of the transom, together with the bent flange, should be cut by 8 mm, and the edge of the engine compartment bulkhead by 3 mm. Accordingly, you need to trim the edge of the side sheets adjacent to the chine, then set the bottom stringers flush with the new bottom surface, and re-rivet the bracket at the transom.
Having assembled the set using temporary M4 bolts, press the skin sheets against it and check the contours of the bottom. To do this, you need to attach a 1.5-2 m long rail with a verified straight edge or a steel ruler to the bottom. Over the entire surface, 1.5 m from the transom, the rail or ruler should fit snugly against the skin. Now you can adjust the bilge angles and keel profile, drill out all the rivet holes to d=4.2 mm, install sealing tape and rivet the seams again, but with rivets of a larger diameter.
This work takes a lot of time, but judging by the fact that many amateurs even manage to lengthen their aluminum boats on their own, which is much more difficult, it can easily be done at home. You can read about how to properly rivet and paint a duralumin boat in the book “300 Tips on Boats, Boats and Motors” (“Shipbuilding”, 1975).
The second way to increase the boat's running trim is to install a transverse step or bow hydrofoil.
The dimensions and installation diagram of the transverse step are shown in the sketch provided. The redan can be made from a sheet of duralumin or another aluminum alloy with a thickness of 1-1.5 mm. Having cut out both halves of the redan, give it a slight concavity by knocking out the sheet with a wooden mallet on the sand or “rolling” it around the pipe. The nose edge of the sheet must be sharpened until the edge fits snugly against the sheathing. The strips that support the aft edge of the redan and connect both of its parts on the keel can be made of hard wood, textolite or light alloy.
Before installation, the redan sheets must be carefully primed on the inside and painted - the space between the boat skin and the redan communicates freely with sea water. The mounting screws must be galvanized steel or stainless steel; the use of non-ferrous metal fasteners will cause corrosion of the sheets. It is recommended to strengthen the attachment of the bow edge to the bottom by gluing it with epoxy glue.
A similar redan can be made solid - from polystyrene foam or wood, glued to a metal sheathing metal that has been cleaned to a shine with epoxy glue. After processing, the outside of such a redan must be covered with a couple of layers of fiberglass.
The arrow-shaped step should take about 90% of the total weight of the boat while moving; this must be taken into account when loading it. The position of the redan shown in the sketch is designed to accommodate the driver in the front part of the cockpit.
It should be noted that the above recommendations were not tested specifically on the MKM boat, but they were well tested and gave positive results on similar boats. Therefore, if the effect of installing a redan turns out to be excessive - the running trim will be too large or the boat will begin to dolphin when not fully loaded (or controlled by the engine tiller), do not be surprised and do not despair. To begin, move the fuel cans forward, try to load the bow trunk, and place the passenger in the bow seat.
If these simple measures do not help, you will have to install transom plates with an adjustable angle of attack (see the mentioned book “300 tips”). By increasing the angle of attack of the plates, it will be possible to redistribute the load between the plates and the transverse step, achieving optimal trim for any case of loading the boat and weather conditions.
Another useful addition for the serial “MKM” is the bilge splash guards, mounted on the sides at a length of 1.95 m from the stem. They can be made from a 1.5X40 strip of light alloy, attached to the body using a solid 20X20 duralumin square or short pieces cut from it. The surface of the splash guards should be inclined downward at an angle of about 10° to the horizontal to more effectively reflect splashes.
The recommendations given should significantly reduce the splashing of the MKM boat while moving and improve its ability to ride oncoming waves. An even more effective measure would be to install a bow hydrofoil (see article by L.L. Heifetz “A boat on one wing” in), however, the manufacture and fine-tuning of such a device is an incomparably more complex matter, not to mention the fact that operating a boat on wing is not possible in every water area.
A useful piece of equipment is an awning that protects the boat's cockpit from splashing in fresh weather. If the boat is steered by the tiller, it is not at all necessary to make the awning high and covering the entire cockpit.
The approximate dimensions of a comfortable awning are shown in the sketch. The canopy's arcs are hinged toward the bow and laid in front of the windshield. While underway, the stern canopy 4 is rolled up and suspended from the arc 3 by ribbons, leaving the cockpit in the stern free to control the boat. When parked, the cockpit can be completely closed, and the height under the awning is sufficient for overnight accommodation on floorboards. Details are given in the book “300 Tips”.
The Yaroslavl Shipbuilding Plant began producing the fairly well-known MKM boat back in 1968; it is known to this day due to its simplicity and high reliability indicators. The boat was produced as an improved version of the Kazanka; the manufacturer chose duralumin as the material. Unlike Kazanka, the new boat has the ability to operate with engines up to 25 hp.
But based on operating experience, it is still unsafe to equip a boat with 25 hp engines. power, because this reduced seaworthiness, and impacts with the bow on the water became more frequent. The result of this was the cockpit getting wet. The boat felt great in calm waters at a distance from the shore of up to 1 km.
“MKM” became an excellent replacement for the “Kazanka” boat, which then turned out to be not safe enough. Also from the previous model, the new product received a body design and even equipment. The main model for the development of the new MKM was the MK-29 boat, which had suitable flat-keeled bottom contours.
The main material was alloy grade D16AT; riveted construction was used. The bottom plating and deck received an average thickness of 1 mm. There is a sufficient engine compartment, when parked, you can easily install an outboard motor, after which the compartment is closed with metal covers. The manufacturer states that the forepeak has a volume of 168 liters, the boat holds water well and is practically unsinkable.
Purpose and history of creation. Advantages and disadvantages of the boat
The MKM brand boat is in great demand among fishermen and hunters, since the transport can be used on shallow rivers and lakes. Due to the fact that it was produced in several cities, you can often hear people using such names as “Kharkovchanka”, “Astrakhanka” and “Yaroslavka” in honor of the manufacturing cities. It is because of this that transport has some differences, since each enterprise manufactured it in its own way, despite the existing scheme. Thanks to this, we were able to see the transport with a certain bend.
The goal of the transport developers was to create a boat made of duralumin. It is this material that does not require high-temperature technical processes. In addition, it had to be folded according to patterns so that it could be produced in small factories or at home, if all the parts were available.
Like any transport, the MKM boat has its advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of the vehicle include:
- Weight and capacity.
- Strength.
- Stability in calm water.
As for negative factors, there are two of them:
- Spray often ends up in the boat.
- Transport behaves terribly on the waves.
Technical characteristics of the MKM boat
The dimensions of the boat play a vital role in its operation, so the MKM boat has a maximum length of 4.1 meters, a width of 1.52 meters, and at the midship the side height is 0.57 mm. If you install the equipment and supplies on the boat, the weight of the boat will be 150 kg.

The dimensions make it possible to accommodate up to 4 people in the boat, because the maximum carrying capacity is 400 kg. The maximum power of the engine used, indicated by the manufacturer, is 25 hp. s, but it was clarified above that it is better to use less powerful motors.
Even with the boat fully loaded and using a 25 horsepower motor, it maximum speed will reach a considerable 32 km/h.
How was the boat created?
The history of the fairly popular MKM boat began back in the 60s, because at that time most fishermen and ordinary users could only use an ordinary cauldron. This option was limited in engine power (up to 12 hp) and did not allow certain tasks to be performed. That is why engineers began developing a new model, and that is why in 1968 the world saw the new MKM motor boat. The Yaroslavl plant was considered the developer, and this invention was based on two models - the Kazanka boat and an older version called MK-29.  Boat MKM The need to create a new boat was clear, because the old version was unsafe and a more reliable alloy was required. Also, if a more powerful motor is used on the Kazanka, it may not withstand such operation. And the new MKM has thought through these nuances, although the general structure of the case remains the same. Differences in the design include more filled-up sides in the inner part of the end, and the bottom also received a flat-keeled shape. Because of the manufacturing plant, fishermen began to call the new boat “Yaroslavka”.
Boat MKM The need to create a new boat was clear, because the old version was unsafe and a more reliable alloy was required. Also, if a more powerful motor is used on the Kazanka, it may not withstand such operation. And the new MKM has thought through these nuances, although the general structure of the case remains the same. Differences in the design include more filled-up sides in the inner part of the end, and the bottom also received a flat-keeled shape. Because of the manufacturing plant, fishermen began to call the new boat “Yaroslavka”.
Thanks to the improved hull, it became possible to install a motor with a power of up to 25 hp on the boat. But users spoke poorly of this decision to install the maximum permissible motor. Indeed, in this case, movement on rivers or small bodies of water was quite inconvenient. In the presence of waves, water entered the cockpit and onto passengers.
Detailed review
If you look at the MKM boat, the photos allow you to highlight the rather well-thought-out shape of the hull; standard factory glass helps a lot in its operation. When buying a boat, be sure to pay attention to its quality and assembly; today, stores offer a huge number of defective or counterfeit models.
A noticeable drawback of the MKM boat can be considered a bottom with a flat deadrise, which was only 2 degrees. Because of this, the stability of the boat was insufficient for some actions on the water. Also about the boat MKM reviews they say that the manufacturer poorly thought out the cheekbones, which are not located high enough.
To solve this problem, it may be necessary to install additional intakes; they reflect splashes and allow you to operate the boat more confidently.

Initially, the boat was developed at the factory for simple purposes, so it is better to travel on small rivers and lakes. For large bodies of water, use with caution and move away from the shore by a maximum of 1000 meters. Before use, it is important to understand that the MKM must be operated at a wave height of up to 30 cm. Otherwise, the procedure will be unsafe, so you should not go out to sea or a large body of water on a boat.
But the shortcomings end there; the boat is really worth attention and is in demand. In a standing position, owners note excellent stability. For example, this is an important indicator for fishermen. For better buoyancy, they decided to place the blocks on the boat in two places.
Boat modification
Over the years of operation, many owners have learned to independently repair and modify MKM boats. In the original version, an excessive bend of the bottom part is proposed, and to get rid of this you can do the following:
- We remove the rivet seams that secure the skin itself, sides and stringers.
- Next, the transom part and the bent element need to be cut by 8 mm, and the existing part of the partition for the engine compartment should be cut by 3 mm.
- Similarly, you can shorten the edges of the side plates, namely those that interact with the cheekbone.
- For some time, you can assemble this kit using bolts; you need to press the sheathing sheets to the kit. Experts recommend using a metal ruler.
- It is imperative to expand the rivet sockets to 4.2 mm.
- Sealing tape is laid and the seams are fixed, always with new rivets.
Seaworthiness characteristics of the MKM boat
When using a large motor and the stated characteristics of the hull, it is better not to use the MKM boat in large waves and at long distances. Fishermen advise using it in still water or completely calm conditions. The seaworthiness is stated as follows:
- Maximum wave height for a boat is 25 cm;
- Optimal bodies of water for use are lakes, small rivers, ponds;
- It is recommended to sail no further than 1 km from the shore;
- The optimal engine power is 18 hp, if more, the ship can easily capsize.
 MKM boat, top and side views The photos of the MKM boat show in as much detail as possible that the shape and size of the vessel are not designed for large waves or long trips. In particular, this is limited by the following design disadvantages:
MKM boat, top and side views The photos of the MKM boat show in as much detail as possible that the shape and size of the vessel are not designed for large waves or long trips. In particular, this is limited by the following design disadvantages:
- complete absence of splash guards;
- minimal deadrise;
- The cheekbones on the boat are located quite low.
The MKM duralumin motor boat, the technical characteristics of which were almost identical to the outdated Kazanka, was produced by the Yaroslavl Shipbuilding Plant in 1968. Its main difference from its predecessor was the possibility of equipping it with an mounted power unit with a capacity of up to 25 horsepower. However, with such a ship, it significantly lost seaworthiness; frequent impacts of the bow on the water occurred, which contributed to the cockpit getting wet. The watercraft can be operated normally only in a calm body of water at a distance of no more than one kilometer from the shore.
Housing design
The duralumin boats in question have an aluminum hull one millimeter thick. The design of the element is made in a traditional style, using the riveting method. A flat bottom with a two-degree deadrise at the transom does not particularly add directional stability to the craft. The bypass cheekbones are located quite low, which practically does not protect passengers from splashes. Some craftsmen independently installed additional fenders of various modifications.
In the area of the stern the sides converge upward. This feature, together with some other design nuances of the hull, constituted perhaps the only advantage of the vessel, expressed in good parking stability. Under the aft seat and in the forepeak there are standard buoyancy blocks for those times.
Internal equipment
Domestic MKM duralumin boats have a design that provides for the placement of the forepeak and the engine part separately from the cockpit. They are separated from each other by waterproof partitions. In the parked position, the power unit can be placed in the appropriate compartment and closed on top with a metal lid. Unsinkability is ensured by a 168-liter forepeak and a voluminous sealed box under the stern.

The vessel is equipped with three transversely installed banks, wind glazing, and slatted wooden slats. A pair of bow benches are equipped with folding backrests. In the bow below the deck there is a recess that acts as a small trunk with a lid and lock.
MKM boat: technical characteristics
This watercraft does not shine with special or outstanding performance. Below are the main parameters of the vessel:
- maximum length/width/height - 4100/1520/570 millimeters;
- the deadrise angle indicator in the bottom part is two degrees;
- maximum power - 25 horsepower;
- weight of the MKM boat with equipment - 150 kilograms;
- load capacity - 0.4 tons;
- passenger capacity - 4 people;
- maximum speed with load is 35 kilometers per hour.
Operation of the vessel in question is allowed at a wave height of no more than 250 millimeters, which significantly limits the places where it can be used. The optimal power unit is a motor with a power of 12 to 18 horsepower. Most users and experts agree that the size of the MKM boat, combined with its low seaworthiness, makes its design extremely unsuccessful. However, the vessel is quite suitable for stationary fishing and short distance walks.

Modification and repair of MKM boats
The characteristics of a swimming device can be improved independently in several ways. To eliminate excessive bending of the bottom part, it is necessary to remove the rivet seams that secure the bottom plating, the sides along the cheekbones, and the stringers with the keel. The procedure should be performed from the transom to the second frame of the stern.
The transom lower edge, together with the bent element, is cut by 8 millimeters, and part of the partition of the engine block is cut by 3 mm. Using the same principle, the edges of the side plates interacting with the cheekbone are shortened. The stringers settle flush with the new bottom plane and are riveted into place as part of the transom.
The kit is temporarily assembled with bolts, and skin sheets are pressed against it while controlling the contours of the bottom. A one and a half meter strip or metal ruler is suitable for this. Over the entire area at a distance of 1.5 meters from the transom, the measuring device should fit as closely as possible with the skin. Next, the bilge angles and the keel profile are adjusted. In this case, the rivet sockets must be expanded to a diameter of 4.2 mm, sealing tape must be laid and the seams must be secured with new rivets.

Second tuning method
The MKM boat, the technical characteristics of which leave much to be desired, can be improved on its own by installing a transverse step. This element can be made from duralumin or a similar sheet alloy one and a half millimeters thick. After preparing both parts of the part, it is necessary to give it a concave shape by tapping it with a wooden hammer.
The nose edge of the redan is processed in such a way as to ensure a tight fit to the skin. Supporting and connecting strips are made of hard wood or textolite. Before making final repairs to MKM boats, the sheets should be primed and painted. Fasteners are taken in the form of screws made of stainless steel or galvanized iron. Additionally, the fixation points can be strengthened using epoxy glue.

The MKM boat, the reviews of which can hardly be called flattering, can be upgraded with the help of additional transom plates with an adjustable angle of attack (in addition to the redan). By adjusting the angle, it will be possible to adjust the load between the plates and the step. This will allow you to achieve optimal trim depending on the load and climatic conditions.
A useful addition to the vessel in question will be bilge fenders against splashes. They are mounted on the sides two meters from the stem. The parts can be constructed from a light alloy strip mounted on the body using an alloy square or parts cut from it. To more effectively reflect splashes, the surface of the fenders should look down at an angle of 10 degrees.
Conclusion
The domestic MKM duralumin boat, the technical characteristics of which are practically no different from its predecessor called “Kazanka,” has not found much popularity among the population. The only advantageous difference is the possibility of installing a more powerful outboard motor. The boat in question can be operated with motors of the “Moscow” and “Veterok” types.

The main purpose is amateur fishing and walks in quiet bodies of water near the shore. Despite all the shortcomings of the boat, this vessel also has fans. With a little skill and effort, you can modernize and improve its seaworthiness. In its standard version, the MKM does not have any special qualities that would allow this vessel to be preferred over other boats of a similar class.
Motor boats are the most common means of transportation on small bodies of water, as well as on coastal areas seas and oceans. The convenience of this type of transport lies in the fact that the vehicle itself is relatively inexpensive, and, in addition, does not require large expenses for fuel or components. The boat can freely deliver several people to the right place in the shortest possible time, and even a child can master its control. Most often such transport is used for sea trips, patrolling the territory, as well as for fishing.
The MKM boat is one of the most prominent representatives of this category of transport. The thing is that it successfully combines several very valuable technical qualities that are in demand among domestic clients. It is worth noting that today on the market you can find large number defective or counterfeit products. So you should only buy those boats that have passed certification, and even better, contact branded distributors of these products.
Technical characteristics of the boat "MKM"
In short, all data about this vehicle can be presented in the following form:
- greatest length – 410 centimeters;
- maximum width – 152 centimeters;
- side height at the center – 57 centimeters;
- the bottom deadrise angle at the transom is 2 degrees;
- estimated weight including equipment and supplies – 150 kilograms;
- load capacity – 400 kilograms;
- passenger capacity – 4 people;
- the maximum power of the installed engine is 25 horsepower;
- maximum speed with the most powerful engine and full load is 32 kilometers per hour.
 Useful improvements to the MKM boat
Useful improvements to the MKM boat General description of the boat
This model of motor boats began to be produced in the sixties of the last century. More than old sample– motor boat “MK29”.
By the way, MKM inherited a large number of details and features from this model. In particular, the contours. The main reason for the creation of such boats was the moral and physical obsolescence of the Kazanka boat models, which could only work with engines with a power not exceeding 12 horsepower.
Nevertheless, the arrangement of the MKM for a more powerful engine created its own difficulties. In particular, the problem of moving on rough water surfaces arose. This boat can only be used in almost complete calm, since oncoming waves hitting the bow with force will splash almost everything inside, and, in particular, the cockpit. Of course, passengers will also not be in the most comfortable conditions.
MKM boat hull
The boat's hull is entirely made of duralumin alloy and has a thickness not exceeding one millimeter. The structure itself, as was customary in those years when it was just being developed, was made using rivets. Among the characteristics of the MKM boat, one cannot fail to note the bottom, which was characterized by a flat deadrise with a corresponding indicator not exceeding two degrees. Of course, this has a very negative impact on the stability of the boat. 
A significant drawback of the boat is also its extremely low cheekbones. They provide virtually no protection against splashes, which is why many owners try to solve this problem on their own. Additional intakes are installed near the sides, which serve as splash deflectors.
It is worth noting, however, undeniable advantage boats of this model. They have incredible stability when stationary, which is a very important factor in user comfort during operation.
The fact that the sides converge at the top of the stern contributes to this perfectly. In addition, blocks providing buoyancy are located in two places on the MKM boat.
Seaworthiness of the boat "MKM"
The use of the MKM motor boat is significantly limited by the wave height on the water surface. If this indicator exceeds 30 centimeters, this means that operation is not recommended, as it may be unsafe. Of course, this narrows the range of cases and situations when this boat can go out to sea, or swim along a wide river or large lake.
In addition, if the required amount of horsepower is even slightly exceeded, the boat may begin to behave completely inadequately, and at the same time all safety indicators will significantly decrease. That is why the main area of operation of this kind of equipment is short-term walks along the coastal zone and small bodies of water, as well as stationary fishing in these very small bodies of water. In addition, it performed well on small rivers.